Your Guide to an Operational Risk Management Framework
- Marketing Team

- Nov 29, 2025
- 15 min read
Updated: Dec 1, 2025
An operational risk management framework (ORMF) is the structured approach an organization uses to identify, assess, and neutralize the risks baked into its own internal operations. Think of it as a business's blueprint for catching potential failures in its people, processes, and systems before they blow up into financial or reputational disasters.
A Blueprint for Business Resilience
Imagine trying to build a skyscraper without a detailed architectural plan. You might get the foundation poured, but pretty soon, walls would be misaligned, plumbing would end up in the wrong places, and the entire structure would be dangerously unstable. An operational risk management framework is that essential blueprint for your business. It provides the structure, rules, and tools needed to build a resilient and stable organization.
Without a framework, managing risk is just chaotic, reactive guesswork. Departments end up using different methods to track threats, creating confusing data silos. What one team calls a "high risk" might be another's "medium," making it impossible to get a clear, company-wide view of what could go wrong. The whole point of an ORMF is to replace that chaos with a consistent, disciplined process.
Beyond a Simple Checklist
An effective framework is so much more than a dusty binder of rules sitting on a shelf. It’s a dynamic system that weaves itself into the daily rhythm of the business, helping leaders make smarter, more informed decisions. At its heart, building this system requires understanding the key distinctions between policies and procedures, which form the documented core of the framework.
This system is designed to answer a few critical questions proactively:
What could go wrong? This means identifying every potential risk, from a critical system failure to an internal fraud scheme.
How bad could it be? Here, you’re assessing the potential blast radius of each risk on your finances, reputation, and operations.
What are we doing about it? This is where you implement controls and mitigation strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of a failure.
Is it working? You must continuously monitor how effective those controls are and report on the organization's overall risk profile.
An operational risk management framework transforms risk from an unpredictable threat into a managed variable. It shifts an organization's posture from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention, building a foundation for sustainable growth and stability.
By creating a common language and a standardized process for managing these uncertainties, the framework gets everyone—from the front lines to the C-suite—aligned toward the shared goal of operational integrity. If you're looking to build a foundation in this area, you can explore the core principles of risk management at https://www.logicalcommander.com/post/risk-management to better understand these concepts. This structured approach not only protects the organization from losses but also builds trust with customers, investors, and regulators who see a business that is in control of its own destiny.
The Pillars of an Effective Framework
An operational risk management framework isn’t some static document you file away. Think of it as a living, breathing system built on several interconnected pillars. Each one supports the others, creating a structure that shifts your organization from a reactive, firefighting mode to a proactive, preventive one.
Much like an architect uses support columns to hold up a building, a risk manager designs these components to handle the weight of uncertainty.
These pillars provide the blueprint for figuring out what could go wrong, sizing up the potential damage, and putting measures in place to stop it from happening—or at least soften the blow. They create a continuous cycle of improvement, making sure the framework evolves as your business and its risk landscape change.
This visual breaks down how an operational risk management framework is really all about managing the risks that bubble up from people, processes, and systems.
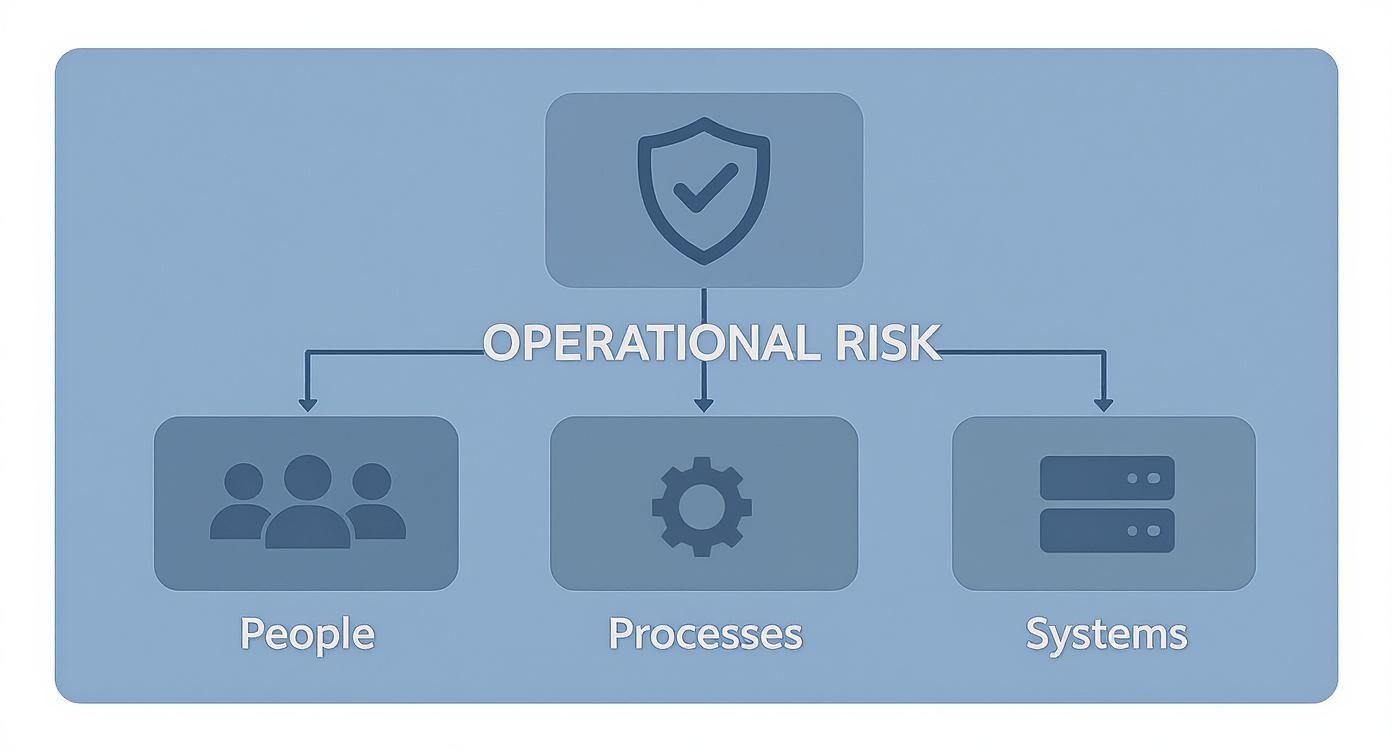
The image drives home a key point: a framework is a protective shield. Its strength depends entirely on how well it governs the interplay between these three core operational elements.
Governance and a Risk-Aware Culture
The bedrock of any successful framework is strong governance. This is more than just committees and rulebooks; it’s about setting up crystal-clear accountability and weaving risk awareness into the company’s very DNA. When governance is strong, everyone from the boardroom to the front lines understands their role in managing operational risk.
This pillar ensures risk management isn't some siloed activity handled by a small team. It becomes a shared responsibility. A key part of this foundation is setting clear guidelines, often by creating a comprehensive Risk Management Policy. This document sets the tone from the top, spelling out the organization’s commitment to getting ahead of risk.
A healthy risk culture also encourages people to speak up about potential problems without fearing blame. When your team feels safe enough to report a near-miss or a flawed process, the organization gets priceless data to prevent a future disaster.
Risk Identification and Assessment
You can't manage a risk you don’t know exists. Simple as that. This pillar is all about systematically hunting for potential operational risks across every part of the business. The goal is to build a complete inventory—often called a risk register—that documents threats before they have a chance to materialize.
The methods for finding them can vary, but usually include a mix of:
Workshops and Brainstorming: Getting cross-functional teams in a room to game out "what if" scenarios.
Process Mapping: Drawing out workflows to spot weak links or potential points of failure.
Loss Data Analysis: Digging into past incidents, both internal and external, to learn from what went wrong.
Once you’ve identified the risks, you have to assess them to understand how bad they could be. This comes down to two key questions: what’s the likelihood of this happening, and what’s the potential impact if it does? This assessment process helps you prioritize, letting you focus your attention and resources on the vulnerabilities that matter most.
Controls and Mitigation Strategies
Okay, so you’ve found and sized up your risks. Now what? The next logical step is to do something about them. This pillar is all about designing and implementing controls—the specific actions, policies, and procedures you put in place to dial down a risk’s likelihood or impact.
Controls aren't a one-size-fits-all solution. They have to be tailored to the specific risk they’re meant to handle. For example, the control for a cybersecurity threat (like rolling out multi-factor authentication) looks completely different from the control for a human error risk (like requiring a second pair of eyes on critical transactions).
A control is your active defense against a known threat. Without effective controls, a risk register is just a laundry list of problems with no solutions. Mitigation is what turns awareness into action.
Effective mitigation requires a clear strategy. Some risks you might avoid entirely. Others, you can reduce to an acceptable level. In certain cases, you might transfer the risk through insurance or simply accept it if the cost to fix it outweighs the potential loss.
Monitoring and Reporting
An operational risk management framework is a living system, and it needs constant attention to stay healthy. The monitoring and reporting pillar ensures the whole structure remains effective over time by keeping a close watch on risk exposure and how well your controls are performing. One of the main tools for this is a set of Key Risk Indicators (KRIs).
Think of KRIs as your early-warning system. A sudden spike in employee overtime could be a KRI for burnout and potential human error. A rising number of customer complaints might be a KRI for a failing process.
This ongoing monitoring feeds into meaningful reporting. These reports need to be clear, concise, and tailored to the audience, giving senior leaders and the board the insights they need to make smart strategic moves. This focus is shifting from pure compliance to strategic decision-making. In fact, a 2025 survey found that only 25% of banks now see regulatory compliance as their main goal for risk management. Instead, they’re zeroing in on liquidity risk (80%) and earnings impact (77%), proving that frameworks are now being used for strategic planning.
Escalation and Remediation
When a control fails or a KRI breaches its threshold, a fast and clear response is everything. This pillar establishes predefined pathways for escalating issues to the right people for swift action. Without clear escalation protocols, critical problems get stuck in red tape, turning a manageable hiccup into a full-blown crisis.
Escalation makes sure risks are handled at the right level of authority. A minor process slip-up might be dealt with by a team manager, but a major data breach needs immediate C-suite and board-level attention.
Once an issue is escalated, remediation kicks in. This is the process of fixing the immediate problem and—more importantly—digging into the root cause to stop it from ever happening again. An effective remediation process creates a feedback loop that improves risk identification, assessment, and control design, making the entire framework stronger with every lesson learned.
How to Put Your Framework Into Action
A framework on paper is just a document; a living, breathing framework is a strategic asset that protects your business. Turning theory into practice is where the real work begins, and it’s where a good operational risk management framework proves its worth. This isn't about flipping a switch—it’s a methodical journey that rests on three foundational pillars: People, Process, and Technology.

Successfully launching your framework means having a thoughtful roadmap. It’s about cultivating the right mindset in your teams, defining clear rules of engagement, and giving everyone the right tools for the job. Get these three things right, and the framework will become embedded in your operations, not just layered on top.
Cultivating Your People and Culture
Let’s be clear: your framework is only as strong as the people who use it. Technology can automate tasks, but it can't create a culture of vigilance. Fostering a risk-aware mindset is the most critical—and often the most challenging—part of implementation.
It all starts with dedicated training that goes way beyond a one-time webinar. Your teams need to understand not just the "what" but the "why" behind the framework. Use real-world examples that connect to their specific jobs to show how identifying and reporting risks actually protects them and the company.
Communication has to be consistent and it must come from the top. When leadership openly discusses operational risk and celebrates proactive risk management, it sends a powerful message. The goal is to create an environment where an employee who flags a potential process flaw is seen as a hero, not a troublemaker.
Defining Your Processes and Policies
With a risk-aware culture taking root, the next move is to codify your approach with clear, unambiguous processes. This is where you translate the high-level goals of your operational risk management framework into concrete, day-to-day actions.
This boils down to a few key steps:
Define Your Risk Appetite: You have to clearly state the types and amount of operational risk the organization is willing to accept to hit its goals. This becomes the north star for every risk-related decision you make.
Establish Clear Policies: Develop and document formal policies for how you’ll handle risk identification, assessment, control testing, and reporting. Make sure these are dead simple for every employee to find and understand.
Map Critical Workflows: Visually map out your most important business processes to pinpoint inherent risks and control points. This exercise almost always uncovers vulnerabilities you never even knew you had.
These defined processes are the guardrails that keep your operations from running off the road. If you're looking to strengthen this area, exploring modern internal control best practices can provide valuable insights into building robust and effective process-level defenses.
Leveraging the Right Technology
Not long ago, managing operational risk was a manual, spreadsheet-driven nightmare. Today, technology is a powerful ally, automating the tedious work and providing insights that would be impossible to gather by hand. Modern Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms act as the central nervous system for your framework.
These systems can:
Automate the distribution and tracking of risk and control self-assessments (RCSAs).
Monitor Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) in real-time and fire off alerts when thresholds are breached.
Provide dynamic, role-based dashboards that give every stakeholder a clear, immediate view of the risk landscape.
The right technology doesn’t replace human oversight; it supercharges it. It frees up your risk team from administrative grunt work so they can focus on high-value strategic analysis and advisory work.
The market trends tell the whole story. The global operational risk management market recently hit US$10.5 billion and is projected to reach US$23.7 billion by 2028. This explosive growth shows that organizations now see robust operational risk management as a key competitive advantage, not just another compliance checkbox.
A phased rollout is almost always the smartest play. Start with a pilot program in a single department to test out your processes and tech. This lets you work out the kinks on a smaller scale, gather real feedback, and build a success story you can use to drive adoption across the rest of the organization.
Integrating Your Framework Across the Business
An operational risk management framework can't live in an ivory tower. Its real power is unleashed when it moves beyond the risk team and gets woven into the very fabric of your organization. Think of your framework not as a rigid set of rules, but as a central hub, constantly sharing data and receiving intelligence from every critical business function.
This is how you break down the departmental silos that so often hide emerging threats. When functions like Human Resources, Legal, and Internal Audit operate on their own islands, crucial risk signals get lost in the shuffle. A truly integrated framework creates a unified ecosystem where information flows freely, giving you a complete, 360-degree view of operational risk.

Creating a Unified Risk Ecosystem
Building these connections transforms your framework from a passive reporting tool into an active, strategic partner for the entire business. Each department holds a unique piece of the risk puzzle. Integrating them is the only way to see the complete picture.
This synergy also ensures that operational risk management becomes a shared responsibility, not a niche activity confined to one team.
Consider these key integration points:
Human Resources (HR): HR data is a goldmine of leading risk indicators. A sudden spike in employee turnover in a specific department could signal poor management or failing processes—both are significant operational risks.
Legal and Compliance: Regulatory updates coming from the legal team have to flow directly into your risk identification process. This keeps the framework current with new compliance obligations, helping you sidestep costly penalties.
Internal Audit: The findings from internal audits provide a real-world stress test of your controls. Integrating these results allows you to continuously fine-tune your framework based on proven vulnerabilities.
An integrated framework creates a powerful feedback loop. It doesn't just push risk information out; it pulls vital intelligence in from every corner of the organization, making the entire system smarter and more predictive.
Practical Examples of Integration
Let's move from theory to reality. Imagine your HR department flags a 30% increase in overtime hours within your IT security team. In a siloed organization, this is just a payroll issue. In an integrated model, this data feeds into the ORMF as a Key Risk Indicator (KRI) for employee burnout, which is a direct threat to your cybersecurity posture.
Or picture this: the legal department identifies a new data privacy regulation. This automatically triggers a workflow within the framework, assigning tasks to relevant process owners to assess their controls, identify gaps, and implement changes. This proactive connection prevents last-minute scrambles and potential regulatory breaches.
The table below shows just how different departments contribute to—and benefit from—a connected operational risk management framework.
Key ORMF Integration Points Across Departments
This table illustrates how the Operational Risk Management Framework (ORMF) connects with and provides value to other critical business functions.
Department | Integration Point | Shared Goal |
|---|---|---|
Human Resources | Shares data on turnover, training completion, and performance issues. | Identify "people risks" like employee fraud or skill gaps before they cause a loss. |
Legal & Compliance | Provides updates on new regulations and pending litigation. | Proactively adjust controls to ensure the business remains compliant with changing laws. |
Internal Audit | Supplies findings from control tests and process reviews. | Validate the effectiveness of risk controls and pinpoint areas for improvement. |
Information Technology | Reports on system downtime, access violations, and cyber threats. | Connect technical vulnerabilities to their potential business and financial impact. |
By building these bridges, the framework becomes the connective tissue that holds the organization's risk management efforts together. It ensures everyone is working from the same playbook, speaking the same language, and driving toward the same goal: operational resilience. This collaboration amplifies the value of your framework far beyond what any single department could achieve alone.
Navigating Modern Risk and Regulatory Challenges
Building a solid operational risk management framework used to be a straightforward, internal job. Not anymore. Today's risk landscape is a tangled web of interconnected threats, shifting regulations, and sky-high ethical expectations that can overwhelm even the most prepared companies.
Yesterday's siloed approach to risk is completely obsolete.
Risks no longer stay in their neat, predictable boxes. A geopolitical crisis can snap a supply chain, which then creates a cybersecurity vulnerability as teams rush to onboard new, unvetted vendors. This domino effect means your framework has to be dynamic and holistic, capable of seeing how one trigger can set off a chain reaction across the entire business.
This isn't just theory. Research in 2025 involving 47 top banks and insurers confirmed this reality, revealing an increasingly interconnected risk landscape where the lines between categories are blurring. The study made it clear: threats can no longer be assessed in isolation. This forces a fundamental change in how organizations design their risk frameworks. You can discover more insights about these emerging risk categories from the original research.
The Rising Bar of Regulatory Scrutiny
Regulators around the globe are taking notice of this interconnectedness, and they're raising their expectations to match. They’re moving beyond simple compliance checklists and are now demanding proof of genuine operational resilience. You have to show, not just tell, that your organization can withstand, respond to, and recover from a major disruption.
A perfect example is the European Union’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). This landmark regulation imposes tough requirements for ICT risk management, incident reporting, and third-party risk for financial institutions. DORA effectively makes operational resilience a non-negotiable legal mandate, forcing firms to stress-test their systems and prove their frameworks actually work under pressure.
These mandates reflect a broader trend. Regulators now expect you to have a deep, granular understanding of your critical business services and all their dependencies—the people, processes, technology, and vendors that keep them running. This requires a level of detail and integration that traditional frameworks simply weren't built for. A well-designed compliance risk management framework is absolutely essential for meeting these new demands.
Navigating Ethical Gray Areas
Beyond regulatory pressure, a modern operational risk framework has to confront thorny ethical challenges, especially around data privacy and employee trust. As organizations gather more data to manage risk, they walk a fine line between necessary oversight and intrusive surveillance.
For instance, monitoring employee communications to detect potential fraud or misconduct immediately raises red flags around privacy. Your framework must include clear, transparent policies that spell out exactly what is being monitored, why it's being monitored, and how that data is protected and used. Without this ethical foundation, your risk management efforts can quickly demolish employee trust and create a culture of fear.
This is where a principles-based approach becomes so critical. A well-structured framework helps you navigate these issues by:
Ensuring Transparency: Clearly communicating the purpose and scope of all risk management activities to your people.
Defining Boundaries: Establishing strict rules to prevent data misuse and protect individual privacy.
Promoting Fairness: Implementing processes that are applied consistently and without bias across the board.
Ultimately, a modern operational risk management framework has to do more than just protect the company from financial loss. It must also build and maintain trust with regulators, customers, and its own people by navigating this complex new world with both diligence and integrity.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers.
Even with the best game plan, you're bound to have questions when you start putting an operational risk management framework into action. Let's tackle some of the most common ones we hear from leaders trying to get this right.
What’s the Difference Between Operational and Strategic Risk?
This is a great question, and the distinction is crucial. Think of it like this: strategic risk is about picking the right mountain to climb, while operational risk is about having the right gear and skills to get up that mountain safely.
Strategic risk is the danger of making the wrong high-level business decisions—like launching a product no one wants, entering a market you can't compete in, or simply failing to innovate. It’s about the what and why of your business.
Operational risk, on the other hand, is all about the how. It’s the risk of failure in the day-to-day execution of your strategy. This comes from breakdowns in your internal processes, people, and systems. A server crashing during your biggest sales event, a key employee making a critical error, or an internal fraud scheme are all operational failures. The two are deeply linked; a brilliant strategy can be completely derailed by sloppy operational execution.
How Can a Small Business Implement an ORMF?
A small business doesn't need a massive, complicated system designed for a global bank. The trick is to start small and focus on what's absolutely mission-critical for your survival. Forget trying to build a perfect, all-encompassing framework on day one.
Instead, take a practical, step-by-step approach:
Identify Your Core Processes: What are the handful of things that, if they broke, would shut you down? Think processing customer payments or protecting sensitive client data. Start there.
Ask "What Could Go Wrong?": For each of those core processes, brainstorm the failure points. What happens if your payment system goes down? What if a laptop with customer information gets stolen?
Put Simple Controls in Place: Implement basic, high-impact fixes. This isn't rocket science. It could be as simple as mandating two-factor authentication for key accounts, setting up a regular data backup schedule, or cross-training another employee on a critical task so you’re not dependent on one person.
The goal is to plug your biggest holes first. Your operational risk framework can then grow and become more sophisticated as your business scales.
What Are Key Risk Indicators, and Can You Give an Example?
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are the early-warning lights on your business dashboard. They’re predictive metrics that start flashing to let you know that a specific operational risk is becoming more likely. While Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) tell you about past results, KRIs are all about the future.
A KRI doesn't tell you that you've already lost money; it warns you that the conditions are ripe for a loss to happen soon.
Here’s a classic example: a sudden, sustained spike in failed login attempts on your company network is a KRI for a potential cyberattack. In a different context, a sharp rise in overtime hours for a specific team could be a KRI for employee burnout, which dramatically increases the risk of human error. They give you a chance to act before the damage is done.
How Often Should a Framework Be Reviewed?
An operational risk management framework should never be a "set it and forget it" document gathering dust on a shelf. It's a living system that needs regular care to stay effective. You should plan for a full, formal review of the entire framework at least annually.
But that's just the baseline. Different parts of the framework need more frequent attention. Your KRIs, for example, might need to be watched daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the risk. And your risk assessments need to be updated immediately whenever a major business change happens, such as:
Launching a new product or service.
Adopting a new, critical technology system.
Entering a new market or regulatory environment.
The goal is constant vigilance, making sure your framework evolves right alongside your business and the risks you face.
At Logical Commander Software Ltd., we believe in proactive, ethical risk prevention. Our AI-driven E-Commander platform helps you identify early signals of internal threats and misconduct without invasive surveillance, protecting both your organization and your employees. Know First, Act Fast with Logical Commander.
%20(2)_edited.png)
