6 Types of Integrity Test Sample Questions for 2025
- Marketing Team
- Oct 17, 2025
- 13 min read
Updated: Dec 17, 2025
Hiring decisions carry immense weight. A single internal breach can erode trust, incur massive costs, and damage your brand's reputation. Traditional screening methods often fall short, failing to identify subtle risk indicators related to unethical behavior. This challenge is precisely what Logical Commander solves with an AI-powered, ethical approach to internal risk management. For organizations committed to upholding the highest standards of compliance and ethics, understanding the nuances of different assessment types is paramount for building a resilient workforce.
This guide moves beyond theory to provide a practical breakdown of key integrity test sample questions. We will analyze the structure, strategic purpose, and interpretation of six distinct assessment models, from overt and personality-based tests to situational judgment scenarios. Understanding how to structure these assessments is key. By examining these examples, you will gain actionable insights to strengthen your hiring and internal risk management protocols, creating a framework that is both effective and compliant with EPPA, GDPR, and other privacy regulations. Our goal is to equip HR, compliance, and security leaders with the knowledge to build a workforce founded on strong ethical principles, using tools that are both effective and respectful of individual privacy.
1. Overt Integrity Test Sample Questions: The Direct Approach to Ethical Attitudes
Overt integrity tests, sometimes called "clear-purpose" tests, are direct assessments that explicitly measure a candidate's attitudes toward honesty, theft, and counterproductive workplace behaviors. Popularized by pioneers like John E. Reid and Associates and the Stanton Corporation, these tests ask straightforward questions about an individual's past behaviors and their tolerance for unethical actions in others. This method serves as a foundational layer in a modern, AI-powered risk management framework.
The primary goal isn't to trick a candidate into a confession. Instead, it’s to establish a clear, self-reported baseline of their ethical framework. By analyzing the patterns in their answers, organizations can gauge a candidate's understanding and alignment with core corporate values before they are hired.
Strategic Analysis & Breakdown
Overt tests are most effective when used as an initial filter rather than a definitive pass-or-fail mechanism. The strategy is to identify candidates whose stated attitudes are in stark contrast to the organization's ethical standards. For instance, a candidate who expresses high tolerance for a coworker stealing office supplies presents a different risk profile than one who believes all rules must be followed without exception.
These initial signals are valuable data points. When integrated into a sophisticated system like Logical Commander’s E-Commander, they can be correlated with other behavioral risk indicators post-hire. This transforms a simple pre-hire questionnaire into a crucial element of a long-term, ethical human capital risk management strategy, all while operating under strict EPPA and ISO 27001 guidelines. Our privacy-first design ensures data is handled responsibly, building trust from day one.
Proven Impact and Key Metrics
The effectiveness of overt integrity tests is well-documented, particularly in industries like retail and banking where internal theft is a significant concern. Studies have shown that companies implementing these tests see a measurable reduction in counterproductive behaviors.
The following chart visualizes the efficiency and impact of overt tests.
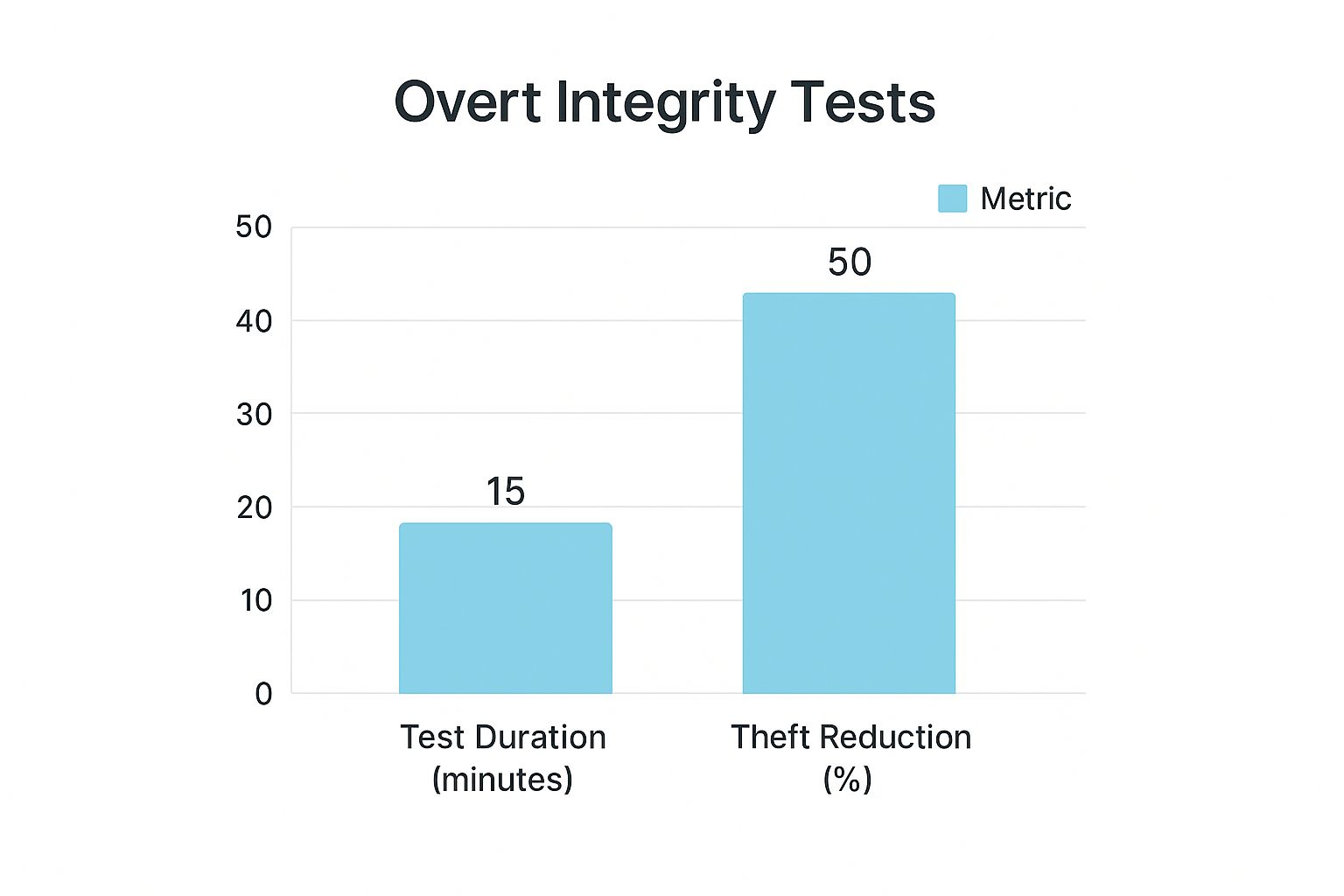
This data highlights a key benefit: a relatively small time investment during the hiring process can lead to a significant reduction in financial and reputational losses from internal theft. By understanding these metrics, organizations can better justify integrating this integrity test sample into their broader strategy for mitigating unethical behavior at the workplace.
2. Covert (Personality-Based) Integrity Tests: The Indirect Measure of Character
Covert integrity tests, also known as personality-based measures, indirectly assess a candidate's reliability and ethical inclinations by evaluating stable personality traits. Research from pioneers like Dr. Joyce and Robert Hogan, along with meta-analyses by Dr. Deniz Ones, established strong correlations between traits like conscientiousness, agreeableness, and emotional stability with counterproductive workplace behaviors.

Unlike their overt counterparts, these tests don't ask direct questions about theft or dishonesty. Instead, they measure underlying dispositions. This indirect approach makes them less susceptible to faking, as the connection between the questions and integrity is not obvious to the test-taker, providing a more candid view of their potential behavior.
Strategic Analysis & Breakdown
The primary strategy behind covert tests is to build a predictive model of on-the-job behavior based on well-established personality frameworks. For example, major airlines use personality-based screening not just for customer service aptitude but to identify individuals with the high conscientiousness and emotional stability required for safety-critical roles. A low score in these areas could indicate a higher risk of negligence or poor impulse control under pressure.
These tests provide a nuanced data layer that complements other assessment methods. When integrated into an advanced AI-powered risk management system like E-Commander, these personality markers serve as a baseline. This allows the system to ethically monitor for behavioral deviations post-hire, transforming a pre-hire integrity test sample into a dynamic component of an ongoing human capital risk management strategy that is fully compliant with EPPA and GDPR. Our system focuses on ethical consistency, not personality judgments, ensuring non-intrusive analysis.
Proven Impact and Key Metrics
The value of covert tests is most evident in roles where reliability, self-control, and conscientiousness are paramount. In industries like healthcare and manufacturing, organizations using assessments such as the PDI Employment Inventory have seen measurable decreases in accidents, absenteeism, and disciplinary actions. The focus shifts from merely screening out "bad apples" to proactively identifying candidates with the inherent traits for long-term success and reliability.
By identifying candidates whose personality traits align with ethical and productive conduct, organizations can build a more resilient and dependable workforce. This proactive approach to team building is a cornerstone of modern, AI-enhanced internal risk mitigation and is crucial for creating a sustainable culture of integrity. To see how these insights can be applied in real-time, you can Request a demo of our E-Commander platform to learn more.
3. Situational Judgment Tests (SJTs) for Integrity
Situational Judgment Tests (SJTs) move beyond attitudes to assess practical application, presenting candidates with realistic workplace scenarios that involve ethical dilemmas. Pioneered by researchers like Dr. Michael McDaniel, these tests measure a candidate's judgment and decision-making by asking them to select the most appropriate response from a set of options. This method evaluates how an individual's ethical reasoning translates into action.

The primary goal is to simulate the complex, nuanced ethical challenges employees face daily. By analyzing how a candidate navigates these scenarios, organizations can predict their likely behavior in similar real-world situations, making SJTs a powerful tool for proactive human capital risk detection. This approach helps identify individuals whose judgment aligns with the organization's compliance and ethical standards.
Strategic Analysis & Breakdown
SJTs are most effective when tailored to the specific risks and ethical culture of the organization. The strategy is to create scenarios that reflect genuine critical incidents, such as a government agency testing a candidate's response to a potential conflict of interest or a pharmaceutical company assessing how a sales rep handles pressure to misrepresent product information. These are not just hypothetical questions; they are carefully designed behavioral simulations.
The insights from an SJT offer a preview of a candidate’s problem-solving and integrity. For instance, a candidate in a financial services compliance test who consistently chooses the path of least resistance over the ethically correct but more difficult option reveals a specific risk profile. These results become invaluable data points for a holistic, AI-powered internal risk management framework that enables cross-departmental collaboration between HR, Compliance, and Legal teams.
Proven Impact and Key Metrics
The impact of well-designed SJTs is significant, particularly in regulated industries and public sector roles where sound judgment is paramount. Organizations using customized SJTs report higher rates of successful hires who demonstrate strong alignment with corporate values and ethical guidelines. They also see a reduction in compliance breaches and employee misconduct.
The key metric for SJTs is not just a "score," but the pattern of judgment it reveals. This qualitative data is crucial for building a workforce that not only knows the rules but has the ethical fortitude to apply them under pressure. When integrated into an advanced platform like Logical Commander’s E-Commander, these patterns help build a comprehensive, privacy-first view of organizational risk.
4. Conditional Reasoning Tests (CRT): Uncovering Implicit Justification Mechanisms
Conditional Reasoning Tests (CRT), pioneered by Dr. Lawrence James, are sophisticated psychological assessments designed to uncover implicit biases and justification mechanisms people use to rationalize counterproductive behaviors. Unlike overt tests that ask direct questions, CRTs present what appear to be logical reasoning problems. However, the answer options are crafted to reveal a candidate's underlying cognitive biases toward or against unethical conduct.
The core principle is that individuals with a higher propensity for aggression or dishonesty will find rationalizations for such behavior more logical or appealing. This method provides a subtle yet powerful lens into a person's character, revealing predispositions that direct questions often miss. It serves as an advanced layer of analysis within a comprehensive human capital risk management framework.
Strategic Analysis & Breakdown
The strategic value of a CRT lies in its ability to bypass socially desirable responses. Candidates are focused on solving a logic puzzle, not on presenting an idealized version of themselves. This makes it an excellent tool for identifying individuals who might otherwise pass a standard integrity test sample by providing expected, "correct" answers.
For example, a reasoning problem might lead to two plausible conclusions: one based on neutral logic and another based on a "hostile attribution bias" (the tendency to view others as having hostile intentions). A candidate who consistently selects answers rooted in these justification mechanisms presents a higher risk profile for workplace conflict or aggression. When integrated into Logical Commander’s E-Commander, these indicators provide crucial, nuanced data points for a holistic risk assessment, operating under strict privacy-first principles.
Proven Impact and Key Metrics
The impact of Conditional Reasoning Tests has been validated in numerous academic and organizational studies, showing a strong correlation between test results and counterproductive work behaviors (CWB) like theft, sabotage, and policy violations. Organizations using CRTs report a more refined ability to predict which candidates are likely to rationalize unethical actions once on the job.
By identifying the cognitive "seeds" of misconduct, CRTs offer a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to risk mitigation. This pre-hire insight is invaluable for building a workforce that not only understands the rules but is also less inclined to bend them. Integrating this data into an AI-powered platform like Logical Commander’s Risk-HR solution allows for the early detection of human capital risks, protecting both the organization and its employees.
5. Biodata (Biographical Data) Integrity Inventories
Biodata integrity inventories assess a candidate’s past behaviors, life experiences, and historical choices that research has shown to correlate with workplace integrity. Based on the principle that past behavior is a strong predictor of future behavior, these tests delve into a candidate's history to identify patterns consistent with reliability and ethical conduct. Pioneered by researchers like Dr. William Owens and Dr. Michael Mumford, this method provides verifiable and non-verifiable data points about an individual's background.
The core purpose is not to judge personal history but to identify behavioral trends that align with the demands of a high-integrity role. These inventories are powerful because they move beyond stated attitudes and focus on demonstrated life patterns, offering a more objective lens through which to assess a candidate's potential for ethical alignment within an organization.
Strategic Analysis & Breakdown
Biodata inventories are most effective when used for roles requiring a high degree of trust and responsibility, such as in law enforcement, finance, or sensitive government positions. The strategy involves identifying specific, job-relevant historical data that correlates with positive or negative workplace outcomes. For instance, a history of consistent employment and academic achievement may correlate with reliability, whereas frequent, unexplained gaps or a history of disciplinary actions may signal potential risks.
When this historical data is integrated into an AI-powered system like Logical Commander’s E-Commander, it becomes a crucial part of a comprehensive, privacy-first risk profile. The system can ethically analyze these patterns post-hire without intrusive monitoring, ensuring that the initial assessment contributes to a long-term, human-centric strategy for managing internal risk, all while adhering to strict EPPA and ISO 27001 standards.
Proven Impact and Key Metrics
The use of biodata is well-established in high-stakes sectors for its predictive accuracy. Law enforcement agencies, for example, have long used biographical data to predict an officer's career success and ethical conduct. Similarly, financial institutions analyze work history patterns to forecast an employee's reliability and reduce the likelihood of internal fraud.
The key metric is the reduction in negative outcomes, such as turnover, disciplinary actions, and policy violations, among employees selected using biodata inventories. Organizations that implement this method see a tangible improvement in workforce stability and a decrease in counterproductive behaviors. By focusing on proven historical patterns, companies can build a more reliable and ethically consistent team, which is a cornerstone of effective strategies to prevent employee theft.
6. Polygraph and Physiological Integrity Tests
Polygraph tests and other physiological measures assess integrity by monitoring physical responses like heart rate, respiration, and skin conductivity while an individual answers a series of questions. Popularized by pioneers like John Augustus Larson and Leonard Keeler, these tests are based on the premise that deceptive answers produce physiological responses that can be differentiated from truthful ones. Due to significant legal restrictions, particularly the Employee Polygraph Protection Act (EPPA) in the U.S., their use in private-sector pre-employment screening is heavily limited.
However, they remain relevant in specific, highly sensitive contexts such as federal security clearance investigations, law enforcement hiring, and roles involving access to controlled substances. In these legally exempted scenarios, the goal is to verify information and assess an individual's suitability for positions where national security or public safety is paramount. This method represents a high-stakes, specialized form of integrity assessment.
Strategic Analysis & Breakdown
The strategy behind using physiological tests is not just about lie detection; it's about risk mitigation in roles where a lapse in integrity could have catastrophic consequences. For federal agencies or police departments, a polygraph serves as a final, intensive check to corroborate information gathered throughout a comprehensive background investigation. It acts as a powerful deterrent against applicants withholding critical information about criminal history or other disqualifying behaviors.
For organizations operating in legally permitted contexts, the key is strict procedural integrity. The test must be administered by a certified examiner following established protocols from bodies like the American Polygraph Association. Any deviation can invalidate the results and expose the organization to legal challenges. This type of integrity test sample is an outlier, reserved for situations where the potential risk justifies its invasive and controversial nature.
Proven Impact and Key Metrics
The impact of physiological tests is most evident in government and law enforcement sectors, where they are credited with uncovering information that would have otherwise gone undetected. For instance, a candidate for a federal intelligence role might pass all background checks but reveal critical counterintelligence risks or undisclosed criminal activity only during a polygraph examination.
While direct ROI is difficult to quantify, the metric of "disqualifying admissions" is a key indicator of their effectiveness. The primary benefit is the prevention of high-impact negative outcomes, such as placing a compromised individual in a position of trust. This focus on preventing severe, low-frequency events is what justifies their continued use in a very narrow set of circumstances, unlike the broader applicability of AI-powered risk management solutions.
6-Method Integrity Test Comparison
Integrity Test Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Overt Integrity Tests | Low - straightforward to administer and score | Low - cost-effective, quick (15-30 minutes) | Predicts counterproductive work behaviors; theft reduction (35-50%) | Retail, banking, hospitality, security | High face validity; legally defensible; easy to use |
Covert (Personality-Based) Integrity Tests | Medium - requires validation and trained interpreters | Medium-High - longer duration (20-45 minutes); professional interpretation required | Predicts broad work behaviors, both productive and counterproductive | Management, healthcare, aviation, law enforcement | Resistant to faking; better candidate acceptance; multi-purpose |
Situational Judgment Tests (SJTs) | High - scenario development with SME input | High - time-consuming to develop and score | High predictive validity for ethical decision-making in context | Management, compliance, customer-facing roles | Realistic, job-relevant; high face validity; customizable |
Conditional Reasoning Tests (CRT) | High - requires specialized development and expertise | Medium - 20-30 minutes; specialized administration | Measures unconscious biases; predicts unreported counterproductive behaviors | Security clearances, law enforcement, high-security roles | Very resistant to faking; candidates unaware tested traits |
Biodata Integrity Inventories | Medium-High - needs large validation samples | Medium - 30-45 minutes; data-heavy | Prediction based on past behaviors; comprehensive candidate background | Law enforcement, military, financial services, insurance | Strong predictive validity; based on actual past behavior |
Polygraph and Physiological Tests | Very High - requires certified examiners and strict protocols | Very High - 2-4 hours; expensive and intrusive | Detects deception in specific incidents; psychological deterrence | Federal government, law enforcement (limited), security-sensitive roles | Can detect deception in investigations; detailed incident info |
Integrate Your Integrity Strategy with Ethical AI
Navigating the landscape of integrity assessments requires more than just understanding the different types of tests. As we have explored through various integrity test sample scenarios, the real challenge lies in moving from static, point-in-time evaluations to a dynamic, continuous, and ethically grounded strategy. Traditional tests provide a valuable snapshot, but they cannot keep pace with the evolving nature of internal risks. An employee who passes a pre-hire screening can still become a risk months or years later due to changing circumstances. This is where a modern, AI-powered approach becomes essential.
The ultimate goal is not merely to screen for integrity at the hiring stage but to cultivate and maintain an ethical culture throughout the employee lifecycle. This requires a system that can identify subtle shifts in behavioral patterns and risk indicators without resorting to invasive surveillance. A one-off test offers a single data point, whereas an ethical, AI-powered framework provides a holistic and evolving picture of organizational health, delivering real-time detection and a measurable ROI.
From Static Samples to Real-Time Insights
Consider a regulated financial institution that relies solely on pre-employment integrity tests. A new hire passes with flying colors but, six months later, begins experiencing severe personal financial distress. This pressure could create a powerful motive for misconduct, yet traditional systems would remain oblivious until a policy is violated or fraud is committed.
An advanced, ethical AI platform like Logical Commander's E-Commander operates differently. By analyzing metadata and non-intrusive operational data in a privacy-first, EPPA-compliant manner, it can detect anomalies that correlate with heightened risk indicators. Instead of a "pass/fail" judgment, the system provides actionable insights, enabling a manager or HR business partner to engage in a supportive, constructive conversation long before any wrongdoing occurs. This is the critical shift from reactive investigation to proactive risk mitigation and employee support.
Actionable Next Steps for a Unified Strategy
Integrating these insights into a cohesive framework is paramount for building organizational resilience. Mastering this modern approach not only protects against financial and reputational damage but also fosters a culture of trust and psychological safety. Here are your next steps:
Audit Your Current Process: Review your existing use of integrity tests. Identify where the gaps are, particularly the lack of continuous insight post-hiring. Are you only looking at the front door, or are you monitoring the entire house ethically and non-intrusively?
Foster Cross-Departmental Collaboration: True internal risk management is not just an HR or Security function. Use a unified platform like our Risk-HR solution to break down data silos and enable seamless collaboration between HR, Legal, Compliance, and Security. A shared, real-time view of risk is your strongest defense.
Embrace Ethical AI: Shift your mindset from traditional "testing" to continuous, ethical risk analysis. Prioritize solutions that are non-intrusive, privacy-first by design (ISO 27001/27701 certified), and fully compliant with regulations like EPPA, GDPR, and CPRA.
By moving beyond isolated integrity test samples and adopting an integrated, AI-driven strategy, you are not just implementing a new tool; you are future-proofing your organization's ethical foundation and demonstrating a profound commitment to your people.
Ready to transition from static integrity tests to a dynamic, AI-powered risk management strategy? Discover how Logical Commander Software Ltd. transforms internal risk detection with its EPPA-compliant, privacy-first platform that delivers measurable ROI while respecting human dignity. Request a demo of our E-Commander platform today or, for advisors and integrators, join our PartnerLC network to deliver next-generation solutions to your clients.
Know First. Act Fast. Ethical AI for Integrity, Compliance, and Human Dignity.
%20(2)_edited.png)
